World Class Parasites: Volume 10 - Schistosomiasis (World Class Parasites)
Free download. Book file PDF easily for everyone and every device. You can download and read online World Class Parasites: Volume 10 - Schistosomiasis (World Class Parasites) file PDF Book only if you are registered here. And also you can download or read online all Book PDF file that related with World Class Parasites: Volume 10 - Schistosomiasis (World Class Parasites) book. Happy reading World Class Parasites: Volume 10 - Schistosomiasis (World Class Parasites) Bookeveryone. Download file Free Book PDF World Class Parasites: Volume 10 - Schistosomiasis (World Class Parasites) at Complete PDF Library. This Book have some digital formats such us :paperbook, ebook, kindle, epub, fb2 and another formats. Here is The CompletePDF Book Library. It's free to register here to get Book file PDF World Class Parasites: Volume 10 - Schistosomiasis (World Class Parasites) Pocket Guide.
Contents:
These observations exemplify some aspects of the intriguing complexity of the parasite-host relationship established during very long co-evolution Fig. Bloch called attention to an apparent discrepancy in the extent of the attack on schistosomules by granulocytes between the in vivo observations and in vitro studies. The later experiments have repeatedly demonstrated that granulocytes and other cells involve a major number of schistosomules, adhering to them and killing them.
While cell adherence to schistosomules was observed in vivo , the number of schistosomules attacked was small. According to Bloch , the reason for the discrepancy may be that in vivo the parasites are metabolically more active and alter their surface membranes more rapidly, so that cell adherence is not so effective as in in vitro environment. Lozzi et al. However, only in the reinfected animals, were the eosinophils able to adhere to the larval surface, damaged larval being found inside eosinophilic infiltrates. These authors questioned the significance of this adhesion, since it could either signify a role in larval death or a phenomenon secondary to larval degenerative changes.
Why helminths have been responsible for evolutionary pressure to eosinophil response in most of their hosts? Is it any particular type of adaptative immune response Mitchell that favors the host and the parasite? The eosinophil is an ubiquitous cell, able to hide its purposes for more than years thousands or millions of years? What is its role in the normal physiology? To answer this question it will be fundamental to do phylogenetic and in vivo studies, together with molecular biology approaches.
Schistosoma - Wikipedia
In this context, McNagny et al. By analogy to saxiphilin, melanotransferrin may have evolved to bind and inactivate toxic substances present in intestine or generated during kidney filtration or eosinophil maturation.
- Schistosomiasis in Malawi: a systematic review.
- Monkeybug Madness 1.
- Revising Green Infrastructure: Concepts Between Nature and Design.
- Fungal Pathology.
- Introduction.
- The Headless Cupid.
Further experiments are required to elucidate the molecule's true function McNagny et al. In fact, infections by parasites can be useful models to study eosinophil physiology and physiopathology, because the parasites may function as natural eosinophil stimulants or depressors.
According to Samter , eosinophils continue to be "nominated but not elected cells". Actually the function of eosinophils is complex, varied and still unknown, but can be artificially schematized as in Fig. Activation of complement by human eosinophil granule major basic protein. Cyclic eosinophilic leucocytosis in eosinophilic leukemia with observations on transcobalamin I and eosinophils.
Cancer 54 : Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 79 : Molecular evolution of the vertebrate immune system. Proc Nat Acad Sci 91 : Isolation and characterization of major histocompatibility complex class II b genes from the nurse shark. Why do schistosomes have separate sexes? Parasitol Today 6 : Peroxidatic activity of mononuclear phagocytes developing in milky spots. J Reticuloendothelial Soc 28 : Developmental stages and localization of peroxidatic activity in the leucocytes of three teleost species Cyprimus carpio L.
Cell Tissue Res : In vivo microscopy of schistosomiasis.
Schistosomiasis collection at NHM (SCAN)
The dynamics of the host-parasite responses to Schistosoma mansoni in the hypodermal tissues as observed in transparent chambers in two susceptible hosts during primary and challenge infections. Am J Trop Med Hyg 33 : Ultrastructural observations on peritoneal exudate cells from the striped bass. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 12 : Develop Biol 14 : Experimental murine schisosomiasis mansoni: establishment of the chronic phase of the disease. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 87 Suppl. IV : Hepatic eosinophil granulocytopoiesis in murine experimental schistosomiasis mansoni. Br J Exp Pathol 62 : Rev Bras Malariol D Trop 8: Parasites and the language of evolution.
Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, pp. Tissue eosinophil proliferation and maturation in shistosome-infected mice and hamsters. Am J Trop Med Hyg 27 : Effector functions of eosinophils in schistosomiasis. Orchestration, relative contribution, and relationship to macrophage function.
J Immunol : Cross-regulatory role of interferon-gamma IFN- g , IL-4 and IL in schistosome egg granuloma formation: in vivo regulation of the activity and inflammation. Clin Exp Immunol 98 : O parasito - Schistosoma mansoni, p. In AS Cunha, Esquistossomose mansoni. Where do human schistosomes come from?
Perspectives of using Euphorbia splendens as a molluscicide in schistosomiasis control programs. Hepatic granuloma of mice infected with Schistosoma mansoni. Ibrahim, Farouk, In this study, we seek lasting solutions to fight against schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminthiasis in the ecoepidemiological context of a large dam. ENW EndNote.
An evolutionary approach. Trend in Ecol Evol 5 : Ann Parasitol Hum Comp 65 Suppl. I : Invertebrate defense systems - An overview, p. The Reticuloendothelial system - A comprehensive treatise. Vol 3 - Phylogeny and ontogeny. Plenum Press, New York. Ultrastructure of the bone marrow of the salamander Plethodon glutinosus Caudata: Plethrodontidae. J Morphol : Enhancement of urokinase-induced plasminogen activation by the cationic protein of human eosinophil granulocytes.
Main content
Thromb Res 14 : The exploitation of host immune responses by parasites. J Parasitol 73 : Light and electron microscope observations on certain leukocytes in teleost fish. J Cell Sci 17 : Eosinophil-mediated injury to lung parenchymal cell and interstitial matrix. J Clin Invest 74 : The blood cells of the Haitian tarantula and their relation to the moulting cycle. J Morphol 68 : Ultrastructural observation on the granular leucocytes of the tuatara Sphenodon punctatus Gray. Tissue Cell 11 : Studies on the host-parasite relationship in Schistosoma mansoni -infected mice.
The immunological dependence of parasite egg excretion. Immunology 35 : Immunological control of hepatotoxicity and parasite egg excretion in Schistosoma mansoni infections: stage specificity of the reactivity of immune serum in T-cell deprived mice. Mechanisms of Schistosoma mansoni egg excretion: parasitological observations in immunossuppressed mice reconstituted with immune serum.
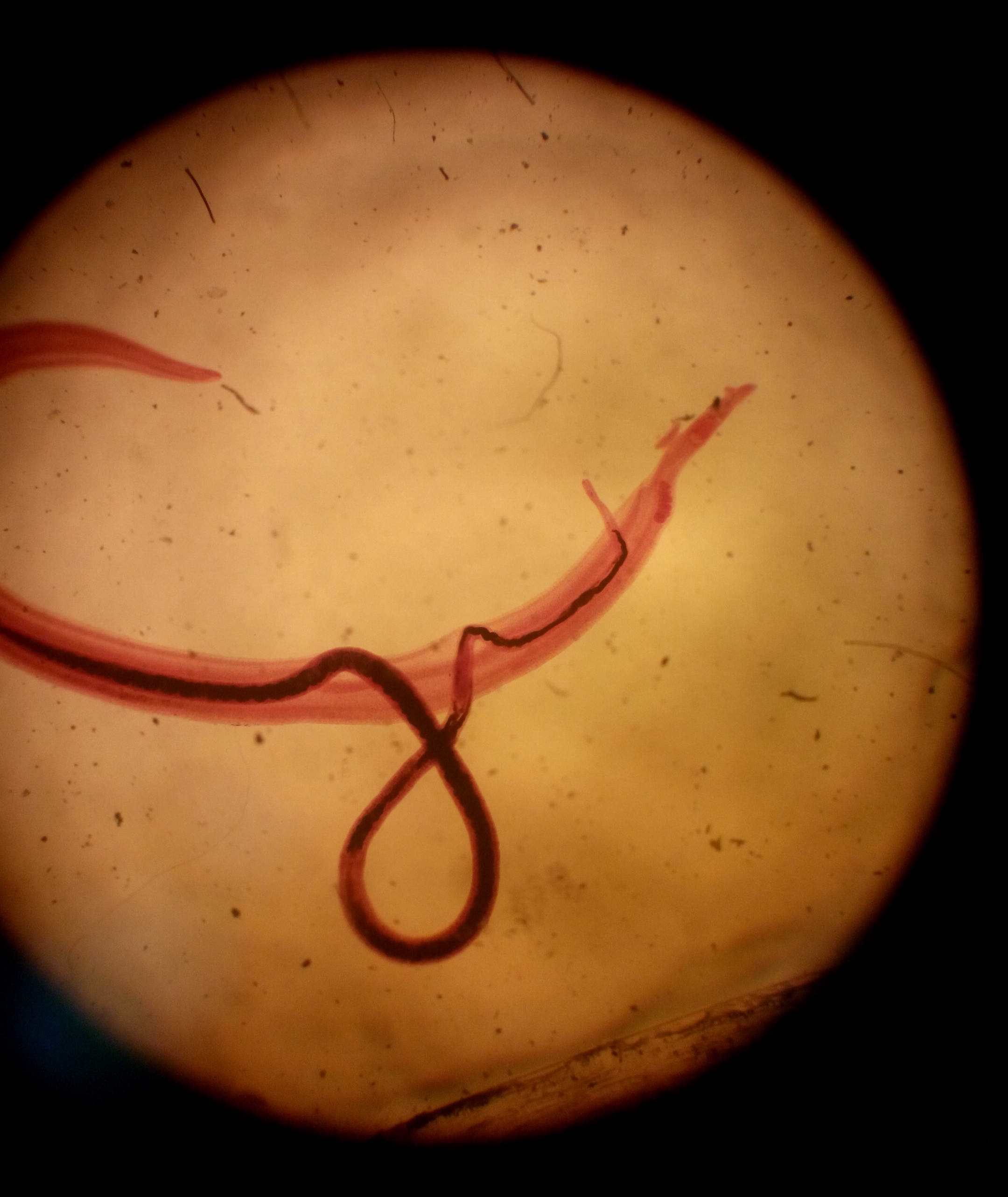
Parasite Immunol 5 : Eur J Immunol 16 : The origin of animal body plans. Am Scientist 85 : Estudios sobre la esquistosomiasis mansoni en Puerto Rico.
- Advances in Information Systems Development: Volume 1.
- Big-data-driven modeling unveils country-wide drivers of endemic schistosomiasis.
- Java Web Services: Up and Running (2nd Edition).
- Intensive Care Nursing.
Estudio biologico. Cytokine regulation of host defense against parasitic gastrointestinal nematodes: Lessons from studies with rodent models. Ann Rev Immunol 15 : Elektronenmikroskopishe untorsuchungen am uterusmuskel der ratte unter follikehormonwirkring.
Introduction
Virchous Arch : Physicochemical and biological properties of the major basic protein from guinea pig eosinophil granules. J Exp Med : Cytochemical identification of the leukocytes of torpedoes Torpedo marmorata Risso and Torpedo ocellata Rafinisque. Basic Appl Histochem 27 : Egg deposition is the major stimulus for the production of TH 2 cytokines in murine schistosomiasis mansoni. The biology of host-parasite relationship among protozoa living in man. Quat Rev Biol 1 : In vivo molecular analysis of lymphokine involved in the murine immune response during Schistosoma mansoni infection.
Type-specific collagen degradation by eosinophils. Biochem J : Immunocompetence in the lowest Metazoan Phylum: transplantation immunity in sponges. Science : Evolution of immunity, p.