Complex Systems: Relationships between Control, Communications and Computing
Free download. Book file PDF easily for everyone and every device. You can download and read online Complex Systems: Relationships between Control, Communications and Computing file PDF Book only if you are registered here. And also you can download or read online all Book PDF file that related with Complex Systems: Relationships between Control, Communications and Computing book. Happy reading Complex Systems: Relationships between Control, Communications and Computing Bookeveryone. Download file Free Book PDF Complex Systems: Relationships between Control, Communications and Computing at Complete PDF Library. This Book have some digital formats such us :paperbook, ebook, kindle, epub, fb2 and another formats. Here is The CompletePDF Book Library. It's free to register here to get Book file PDF Complex Systems: Relationships between Control, Communications and Computing Pocket Guide.
Contents:
Thus it is indispensable for the creation of socially intelligent systems to go far beyond the current state-of-the-art and to be able to detect and categorize a complex set of semantic, pragmatic, stylistic and sentiment oriented dimensions of messages representing and predicting the complex behavior of users in the Internet, the process of formation of collective emotions and their multifaceted impact on user preferences, decisions and actions in the online and offline world. Socially Adaptive Interactive Tools significantly contribute to the creation of sustainable, socio-inspired ICT systems that socially adapt to users, their respective context, and to individual and collective needs.
Socio-Technical Fabric JKU Ensembles of digital artifacts appliances, tools and everyday objects with integrated electronics and communication capabilities as compounds of huge numbers constitute a future generation of socially interactive ICT, to which we refer to as Socio-Technical Fabric, weaving social and technological phenomena into the 'fabric of technology-rich societies'.
Indications of evidence for such large scale, complex, technology rich societal settings are facts like "things" or "goods" being traded in electronic markets today, personal computer nodes and mobile phones on the internet, cars or digital cameras with sophisticated embedded electronics - even for internet access on the go etc. Today's megacities approach sizes of citizens.
Already today some users are registered on Facebook, videos have been uploaded to YouTube, like music titles have been labeled on last. Our research is thus going away from single user or small user group ICT research issues, and is now heading more towards complex socio-technical systems, i. From both theoretical and technological perspectives, socio-inspired ICT moves beyond social information processing, towards emphasizing social intelligence.
Among the challenges are issues of i modeling and analyzing social behavior facilitated with modern ICT, ii the provision access opportunities and participative technologies, iii the reality mining of societal change induced by omnipresent ICT, iv the establishment of social norm and individual respect, as well as v the means of collective choice and society controlled welfare, e.
Self-organizing networked embedded systems KLA are an important enabler for building large complex embedded systems, which are robust, scalable, and adaptive.
- Building a New Generation of Culturally Responsive Evaluators Through AEAs Graduate Education Diversity Internship Program: New Directions for ....
- Computational Research into Complex Systems?
- FuturICT Austria.
- Relationships between Control, Communications and Computing.
- System of systems.
- Unholy War: Terror in the Name of Islam.
The general economic advantages of such an approach will be shorter-time-to-market, reduced system cost, and lower maintenance cost. Such systems will penetrate society via different applications based on basic research results on complex and self-organizing systems. Examples are algorithms for coordinating robots cooperative search missions for micro-copters, surveillance tasks, carpet cleaning robots and self-organizing algorithms for robust sensor networks e. Smart Grid KLA.
What is FuturICT?
The transformation of our energy system to a complex interacting system of all users generators and consumers promises a more efficient and robust provision of energy. To optimize the operation of the system, all its users generators and consumers will be integrated into a smart grid, where local interactions support balancing energy consumption and production based on demand and availability.
Therefore, it is necessary to define interaction protocols, predict network effects and elaborate a model of the users' behavior. This topic connects traditional engineering research with complex systems and social systems. To harvest and integrate the data from heterogeneous sources e. Such a method is evolving in the Linked Data initiative, and various data pools are already published according to their guidelines, e. However, there are many open problems evolving with the deployment of Linked Data on a large scale. Specifically, issues of data extraction, data quality, real-time data, data provenance, data reliability and trustworthiness need to be addressed to allow deriving reliable information from the web of data.
Such deployment will however be necessary to achieve the overall goals of the FutureICT project. This work is complemented with OFAI's longstanding expertise in the development and application of natural language processing and understanding tools being employed for ontology creation and population, as well as for quality and reliabiltiy assessment.
The penetration of ICT systems in people's daily lives is already in an advanced state and it is still progressing. However, trust in such technologies is often a limiting factor in the exploitation of innovations, and trustful data sources are a strong requirement to reach the FuturICT objectives. Approved reliability starting on the sensor level as well as transparency in the complete data collection and processing path are the keys to provide trustable data source infrastructures.
We therefore see the necessity to assess and quantify the reliability of the data and if possible improve it e. Therefore, the following research issues will be targeted:. Complexity in the Social Sciences - the macro-micro-macro link complexity and complexity science have become widely accepted frameworks because they provide concepts needed to investigate and understand systems composed from heterogeneous and interacting entities.
Often systems are considered complex if some degree of unintended order is achieved as the result of interaction. In contrast to neoclassical concepts relying on an invisible hand ensuring that social systems converge toward a stable equilibrium, complexity science is the science of out-of-equilibrium systems.
Complex Systems Design & Management Asia
It takes into account individual and possibly conflicting goals and intentions and explains emergent properties arising from local interactions rather than well-advised interventions of a central planner. It is often criticised that social sciences suffer from a poor level of precision in the theoretical construction and a statistical modeling that is insufficiently theory-driven. Partially this is due to the inadequateness of the methodological toolbox to answer relevant questions.
Empirical approaches typically assume a constant association of cause and effect.
Cybernetics
In real social systems information is transmitted via social networks imposing spatial and temporal constraints on social interactions. Individual behavioural decisions are the outcome of interactions with the partner, friends, colleagues and relatives. The social structure determines the timing and the topology of interpersonal communication and the institutional structure determines the non-personal environment. The institutional structure mostly limits the individuals' ability, feasibility and acceptability to pursue a certain type of behaviour.
Shows the reader how to take advantage of relationships between control, communications and applied computing to produce solutions to a wide range of. Complex Systems by Georgi M. Dimirovski, , available at Complex Systems: Relationships between Control, Communications and Computing of mutual reinforcement between control, computing and communications.
The inclusion of agent based modelling and systematic and comparative investigations offers new possibilities to develop cognitive valid behavioural theories and to speculate on the consequences of alterative micro-macro feedbacks in order to explain observed patterns. To address the issue, we will develop and implement an agent-based model of innovation that can serve as a computational laboratory for simulating innovation arising from knowledge production and exchange processes.
The model will comprise both theoretical underpinnings - from knowledge economics, industrial economics, and social networks - and solid empirical validation to ensure applicability to specific sectoral and spatial contexts.

The interdependence of decisions of the key market players usually leads to complex game-theoretic situations that have ambiguous outcomes. Agent-based modeling is one way to analyze such oligopolistic systems.
We will apply agent based modeling to the field of environmental technologies. The research question is how oligopolistic settings shape the trajectories of environmental innovation processes, particularly focusing on critical bifurcation points and lock-ins that are suboptimal regarding the eventual effects on the natural environment. Using the concept of multi-agent system modeling combined with an interactive stakeholder involvement, we will explore the systemic feedback on infrastructure.
These analyses will be established on different time and spatial resolutions accounting for the spatial as well as the time-dependent constraints shaping the system behavior. Complexity of social interactions TU Wien During the last decade a new sub-discipline of socio-economics has been developed which avoids the core paradigm of equilibrium theory and market forces. The individual addiction to consume alcohol, to smoke, to use illicit drugs etc. While it is well known that the inherent non-linearities of such socio-economic interactions generate complex behavior, including multiple equilibra, persistent limit cycles and chaos, further research is needed in the creation and solution of economic models.
In particular, the economics of crime, and, more generally, of "deviant" behavior provides a field of applications par excellence. To mention only a few key topics: corruption, illicit drug consumption, violence, counter-terrorism etc. Systemic risk in economic systems MUV Starting on a decade background in agent based modeling and experience with institutions and policy makers, we design regulation mechanisms for financial markets. Aim is to increase systemic stability within an ever-evolving system.
These models are based on new developments of co-evolutionary dynamics and fed with massive data from the real economy, the later posing nontrivial ICT issues. Artificial worlds - understanding collective socio-economic behavior MUV Human collective behavior is poorly understood. In particular experimental data on a multi-relational level is hardly available.
Our aim is to use complete information of human artificial societies such as available in massive multiplayer online games to experimentally understand human behavior, herding behavior in particular. We plan to design role playing games as large scale human behavior laboratories.
We aim to understand the minimum multi-relational data structures, necessary to make testable predictions in real world societies.
Navigation menu
Collecting behavioral electronic fingerprints poses highly non-trivial ICT challenges. Multi-relational data analysis in mass-health issues MUV Western public health systems become increasingly expensive, some even non-financeable. The availability of almost complete nation-wide data records of all medical treatments allows for systemic efficiency analysis which allows to base strategic decisions on fully rational and transparent grounds.
These datasets further allow to design early warning and trend identification systems in public health, improving institutional preparedness to act. These analyses rest heavily on recent developments in network theory of time-varying graphs, community detection in particular. Theory of Complex Adaptive Systems MUV We continuously work on methodological progress of quantitatively understanding complex adaptive systems, especially the statistics of correlated and strongly interacting systems, network theory and multi-relational analysis.
Evolution of complex systems KLA, MUV In order to design complex systems, we employ evolutionary algorithms to find the micro-behavior rules, which lead the overall system to the intended macro behavior. This approach is especially important for future networked systems, which are becoming more and more complex, leading to a breakdown of traditional methods for design, implementation and maintenance. We anticipate that the next decade will manifest an equally great focus on the impact of characteristics of the system elements corresponding to the network nodes and links, with interest in both how those characteristics evince dynamic changes in the network structure and how relations in the network influence the system constituents.
We will explore the interplay of node and link properties with dynamical changes in the network structure, with particular focus on development of the network community structure and of those nodes providing a unifying global backbone to the network. This will be applied to understanding politically induced changes in European collaboration networks.
Showing strong competition and interdependencies as well as "knowledge spillovers," the identification and monitoring of new growth opportunities for entering knowledge markets has become increasingly complex through a richly heterogeneous landscape of many institutions and through the continuous adjustment of actors to changing markets conditions.
Dates Started: October, The interferon response circuit: induction and suppression by pathogenic viruses. Some nonlinear dynamical systems, such as the Lorenz system , can produce a mathematical phenomenon known as chaos. Such features include a heavy tail in the degree distribution, a high clustering coefficient, assortativity or dis-assortativity among vertices, community structure and hierarchical structure. The institutional structure mostly limits the individuals' ability, feasibility and acceptability to pursue a certain type of behaviour.
To this end, we will develop new information-theoretic methods for "digital foot-printing" and time-dependent visualization with limited or no evidence for the evaluation of emerging areas. We build upon a hybrid approach of both semantic clustering techniques and generalized relational maps between "co-occurrences" based on historical, contemporary, and simulated future data for respective data categories of input, output, or outcome in knowledge markets. Ultimately, this will directly contribute to illuminating characteristic routes to emerging areas and foster analyzing and discussing institutions, technologies, and social regulations that can facilitate the efficient production and use of knowledge.
A particular strength is the diversity of research issues and at the same time the connectedness of scientists. There exist countless examples of scientific co-operations between the supporting institutions and the expressed willingness to grow together on project oriented science questions. Medical University of Vienna One of the world's leading medical universities. MedUni Vienna is a state-of-the-art research organization with historic track record of more than years. Inter-disciplinary and transnational research are taken seriously by MedUni Vienna.
Complex systems are met in many areas of natural science, mathematics and social science. Fields that specialise in the inter-disciplinary study of complex systems include systems theory, complexity theory, systems ecology and cybernetics.
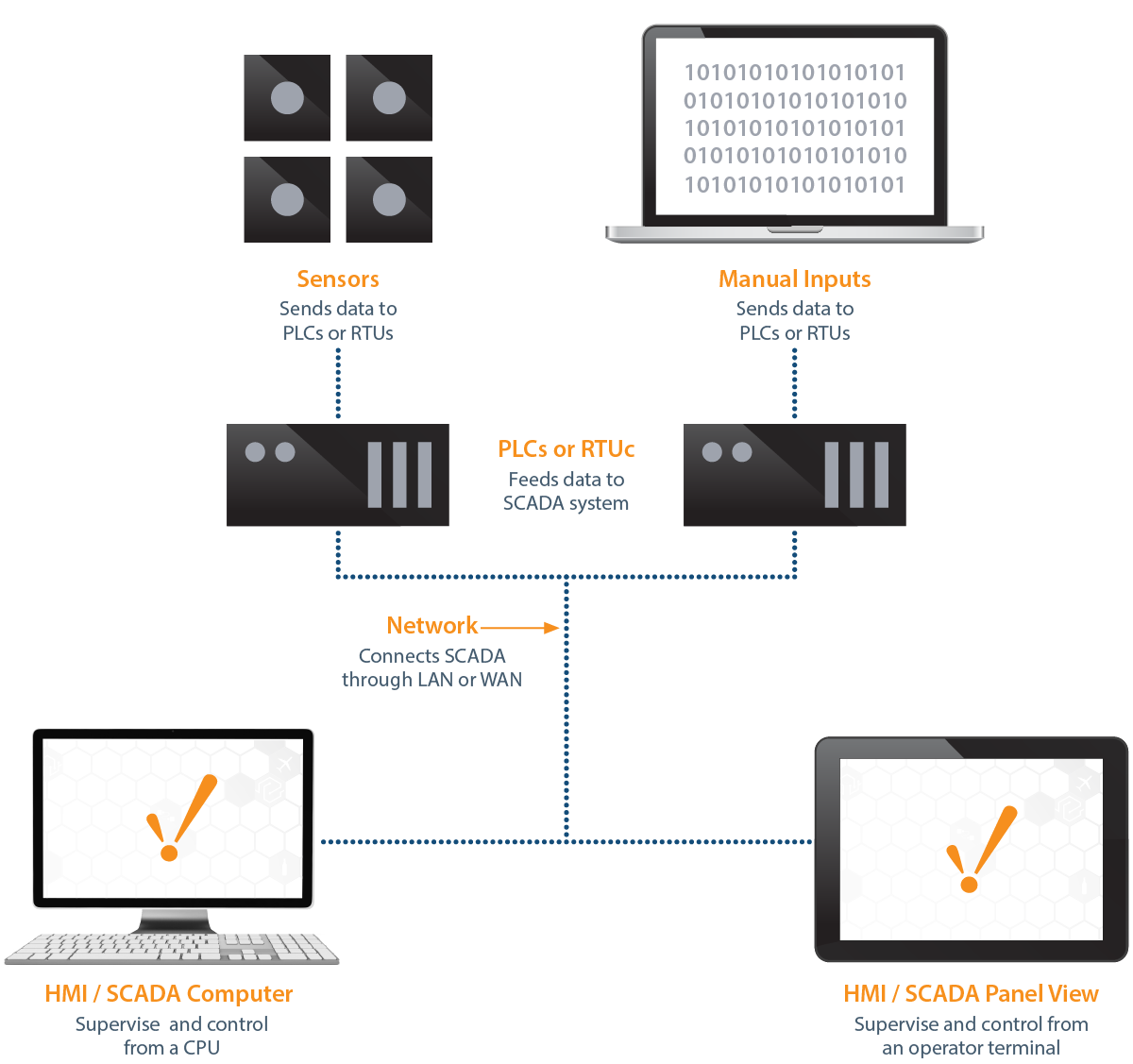
Examples of complex systems with many parts include ant colonies, human economies and social structures, climate, nervous systems, cells and living organisms, including human beings, as well as modern energy and IT infrastructures. Indeed, many systems of most interest to humans are complex systems.
- 1. What are complex systems?.
- Complex Systems.
- Complex Systems: Relationships between Control, Communications and Computing.
- 1. The science of complex systems theory.
- Modelling and Simulation for Autonomous Systems: First International Workshop, MESAS 2014, Rome, Italy, May 5-6, 2014, Revised Selected Papers.
- FuturICT Austria.